Hyperlocal Delivery
In this blog, we explore the intricacies of hyperlocal delivery, the 3 main models, the benefits of using hyperlocal delivery and how technology can be leveraged to make it work.

Hyperlocal delivery is a relatively new term in the logistics industry. This innovative approach to delivery services is designed to cater to customers situated in immediate proximity, promising expedited and efficient delivery solutions.
In the following blog, we will explore the intricacies of hyperlocal delivery, the 3 main models, the benefits of using hyperlocal delivery and finally, how technology can be leveraged to make it work.
The 3 Main Supply Chain Models
Benefits of Hyperlocal Delivery
How Technology Helps Hyperlocal Delivery to Function
What is Hyperlocal Delivery?
Hyperlocal delivery refers to a business model and service that focuses on delivering goods and services to customers within a very limited geographic area. The term "hyperlocal" emphasizes the extremely localized nature of the delivery service, often involving short distances and quick turnaround times. This approach leverages technology, such as delivery driver mobile apps and online platforms, to facilitate the efficient and rapid delivery of products or services to customers in close proximity to the delivery hub. Hyperlocal delivery is often associated with small-scale, local stores and aims to provide convenience and prompt services to customers.
This delivery model is particularly well-suited for businesses such as pharmacies, grocery stores, restaurants, and household services, as it offers a powerful solution to combat inventory spoilage and meet the growing demand for swift and convenient deliveries. In essence, hyperlocal delivery transforms traditional brick-and-mortar establishments into dynamic eCommerce entities. These businesses leverage technology and logistics infrastructure to efficiently manage and fulfill customer orders within remarkably short time frames – often within hours or even minutes. This rapid turnaround time not only enhances customer satisfaction but also addresses the modern consumer's desire for instant gratification and convenience.
The global hyperlocal delivery market has experienced significant growth, underlining its importance in the evolving landscape of commerce. In 2021, the market was valued at an impressive $1.5 trillion, and projections suggest a substantial increase to $5.9 trillion by 2031. This remarkable growth is characterized by a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 14.4%, as reported by Allied Market Research.
SmartRoutes Route Planning Software
Streamline your entire delivery process, all from one platform

The 3 Main Supply Chain Models
1. Aggregator Model
The Aggregator Model is a business strategy that revolves around consolidating various services and goods under a distinct hyperlocal brand, establishing a unique and recognizable identity in the market. In this model, customers interact with a dedicated hyperlocal delivery app, placing their orders seamlessly. The order is then shared with relevant businesses for fulfillment or it can be fulfilled directly by the dedicated app.
For example, Instacart is a prominent player in the hyperlocal grocery delivery industry operating in the United States and Canada. Instacart distinguishes itself by offering same-day delivery services without maintaining any inventory of its own. Instead, it relies on a network of local stores to fulfill customer orders. This involves deploying a workforce known as 'Shoppers' who are dispatched to local stores to collect the items specified in the customer's order. These Shoppers play a crucial role in the fulfillment process, acting as intermediaries between the customers and the businesses providing the goods. The process typically begins with customers browsing the hyperlocal delivery app, selecting their desired products, and placing an order.
The Aggregator Model's strength lies in its ability to offer a wide range of products and services without the burden of maintaining extensive inventories. By leveraging the existing infrastructure of local businesses, this model optimizes efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
2. Inventory-led Model
In the Inventory-led Model, hyperlocal businesses take a proactive approach to managing their inventory, either through direct procurement from local retailers or by producing their own goods. This strategic approach allows them to streamline the entire order fulfillment process, enhancing efficiency and control over the supply chain.
One key aspect of the Inventory-led Model involves establishing direct relationships with local retailers. Hyperlocal businesses engage in the procurement of goods directly from these retailers, creating a mutually beneficial partnership that benefits both parties. By sourcing products directly, businesses can ensure a steady and reliable supply of inventory. This direct procurement also facilitates better negotiation of prices and terms, enabling cost savings and improved profit margins.

Alternatively, some hyperlocal businesses opt to produce their own goods, further consolidating control over their inventory. By manufacturing products in-house, these businesses gain a unique advantage in terms of quality control, customization, and branding. This vertical integration not only ensures a consistent and tailored product offering but also provides a competitive edge in the market.
The inventory-led approach is particularly beneficial for hyperlocal businesses that operate in sectors where demand can be highly variable or where specific and unique products are required. By maintaining their inventory, businesses can respond more effectively to fluctuating market demands, reducing reliance on external suppliers and minimizing lead times in the order fulfillment process.
3. The Hybrid Model
The Hybrid Model represents a versatile approach that offers the strengths of both the Aggregator Model and the Inventory-led Model, blending their respective advantages while mitigating their drawbacks. One notable characteristic of the Hybrid Model is its ability to offer a wide array of products and services through a centralized platform, akin to the Aggregator Model. This allows businesses to tap into a diverse range of offerings without the burden of maintaining extensive inventories. Customers can enjoy the convenience of a comprehensive product selection through a user-friendly interface, placing orders seamlessly via a hyperlocal delivery app.
Simultaneously, the Hybrid Model incorporates certain aspects of the Inventory-led approach by strategically managing its own inventory for specific goods or services. This enables the business to exercise greater control over the supply chain, ensuring the availability of essential items and responding more effectively to fluctuating market demands. By maintaining a curated inventory, businesses can also enhance the overall customer experience by offering unique, high-quality, or exclusive products.
Benefits of Hyperlocal Delivery
More Opportunities for Local Vendors
The ability to offer hyperlocal delivery services is truly a game changer for small-scale businesses, providing them with unprecedented access to the vast landscape of e-commerce and expanding their outreach to a wider customer base. For local vendors who might otherwise face challenges in penetrating the competitive eCommerce market, these services act as a crucial bridge, facilitating the seamless integration of local businesses into the digital realm. By leveraging hyperlocal delivery platforms, local vendors can bypass geographical constraints and gain visibility on a broader scale, breaking free from traditional brick-and-mortar limitations.
Improved Flexibility for Customers
This revolves around empowering customers with the freedom to make purchases on their terms, offering convenience and choice in both the selection of products and the timing of deliveries. Online platforms provide customers with a 24/7 shopping experience, breaking away from the constraints of traditional brick-and-mortar store hours. This flexibility is especially valuable for busy individuals who may have unconventional working hours or limited availability during standard business hours.
Moreover, the convenience extends beyond the shopping experience to the delivery process. Customers have the option to choose delivery windows that align with their schedules, providing a level of customization and control over when they receive their orders. The ability to select specific delivery windows also caters to varying customer preferences. Some may prioritize receiving their orders promptly, while others may prefer deliveries during specific time blocks, such as evenings or weekends. This personalized approach to delivery scheduling enhances the overall customer experience, contributing to higher satisfaction and loyalty.
Cost Efficiency
Cost Efficiency is achieved by eliminating the need for extensive warehousing hubs and large fleets. This approach not only optimizes operational costs but also allows businesses to achieve a low cost per delivery, particularly when catering to nearby customers. Traditional retail models often require businesses to maintain numerous warehouses strategically located to serve various regions. However, by embracing a more centralized and streamlined approach, businesses can consolidate their inventory in a single hub or a limited number of strategically placed hubs. This consolidation minimizes the overhead costs associated with managing and maintaining multiple storage facilities, leading to significant cost savings.

Additionally, the decision to forego the need for large fleets of delivery vehicles plays a crucial role in achieving cost efficiency. Hyperlocal delivery services often leverage more agile and flexible distribution methods, such as utilizing existing local infrastructure or partnering with third-party logistics providers. This eliminates the substantial capital investment required for maintaining and operating an extensive fleet of delivery vehicles.
Improved Sustainability
Sustainability is a fundamental aspect of hyperlocal delivery services, contributing to environmental conservation through a combination of reduced fuel consumption and a smaller carbon footprint. This eco-friendly approach aligns with the growing global emphasis on responsible business practices and addresses the environmental challenges associated with traditional delivery models.
One of the key pillars of sustainability in hyperlocal delivery is the significant reduction in fuel consumption. Unlike traditional delivery models that often involve long-distance transportation from centralized warehouses to various regions, hyperlocal delivery services operate on a more localized scale. By serving nearby customers within a specific geographic radius, the need for extensive fuel usage is minimized. Delivery vehicles cover shorter distances, leading to a notable decrease in fuel consumption per delivery.
Moreover, the smaller carbon footprint associated with hyperlocal delivery is a result of both the reduced fuel consumption and the optimization of delivery routes. Technology-driven route planning and real-time data analytics enable businesses to streamline the delivery process, minimizing unnecessary mileage and idle times. This efficiency not only benefits the businesses by reducing operational costs but also plays a crucial role in decreasing the environmental impact of each delivery.
Customer Satisfaction and Retention
With hyperlocal delivery services, customer satisfaction and retention is significantly enhanced through faster delivery times and increased access to a diverse range of goods. These elements not only meet customer expectations but also contribute to heightened satisfaction, fostering loyalty and retention in a competitive market. One of the primary drivers of customer retention in hyperlocal delivery services is the commitment to faster delivery times. Unlike traditional delivery models with longer waiting periods, hyperlocal delivery aims to fulfill orders swiftly, often within hours of purchase.
The emphasis on faster delivery times is complemented by the convenience of choosing specific delivery windows that align with the customer's schedule. This flexibility further enhances the overall satisfaction of customers, allowing them to seamlessly integrate their shopping needs into their daily routines without disruptions. The convenience of receiving products at a time of their choosing adds an extra layer of value to the customer experience.
How Technology Helps Hyperlocal Delivery to Function
- eCommerce Platforms (e.g., Shopify, WooCommerce): The foundation of hyperlocal delivery starts with robust eCommerce platforms. These platforms enable businesses to establish a digital storefront, showcase their products, manage inventory, and facilitate online transactions. Shopify and WooCommerce, among other e-commerce solutions, offer user-friendly interfaces, secure payment processing, and customizable features that cater to the specific needs of hyperlocal delivery businesses.
- Payment Gateways (e.g., Stripe, PayPal): Seamless and secure payment processing is critical for the success of hyperlocal delivery. Payment gateways like Stripe and PayPal provide a secure online transaction environment, allowing customers to make purchases with confidence. These gateways integrate with eCommerce platforms, ensuring that financial transactions are processed efficiently and securely, contributing to a smooth customer experience.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems: CRM systems play a pivotal role in managing customer interactions and data. For hyperlocal delivery, CRMs help businesses organize customer information, track order histories, and personalize communication. This information is invaluable for providing a tailored experience, managing customer preferences, and fostering long-term relationships. CRM systems enhance customer satisfaction by enabling businesses to understand and meet individual needs effectively.
- Route Planning Software: Efficient logistics and route optimization are crucial for hyperlocal delivery services. Route planning software helps businesses optimize delivery routes, considering factors such as traffic conditions, delivery windows, and the proximity of destinations. This technology ensures that delivery vehicles take the most time-effective routes, reducing fuel consumption, minimizing delivery times, and enhancing overall operational efficiency.
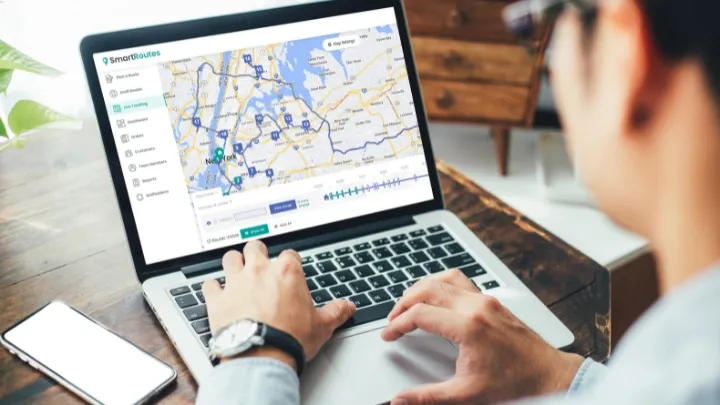

- Mobile Apps and Tracking Systems: Many hyperlocal delivery services utilize mobile applications for both customers and delivery personnel. Customer-facing apps provide an intuitive platform for placing orders, tracking deliveries in real-time, and receiving updates. On the other hand, delivery personnel use apps for efficient route navigation, order updates, and order completion confirmations. These apps contribute to transparency and communication throughout the entire delivery process.
- Data Analytics and Insights: Technology enables hyperlocal delivery services to collect and analyze data. By leveraging data analytics tools, businesses can gain insights into customer behavior, delivery performance, and market trends. This information is invaluable for making informed decisions, optimizing operations, and adapting strategies to meet evolving customer expectations.
How SmartRoutes can Help make Hyperlocal Deliveries Seamless
SmartRoutes empowers delivery teams to create highly efficient routes, optimizing the time it takes to deliver from the store to the customer's address. It minimizes the likelihood of delays and diversions while providing accurate estimated time of arrivals (ETAs). These platforms are instrumental in facilitating multi-drop deliveries, a critical element of hyperlocal operations that ensures the profitability of every delivery. Make sure to take advantage of our 7 day free trial to experience the benefits right now!
Frequently asked questions
1. What is hyperlocal delivery?
Hyperlocal delivery refers to a service model that focuses on providing fast and localized delivery of goods and services to customers within a limited geographic area. It typically involves short delivery distances and aims to fulfill orders swiftly, often within the same day or even hours.
2. Is multi-drop delivery essential for hyperlocal operations?
Yes, multi-drop delivery is often considered essential for hyperlocal operations. It involves delivering multiple orders to different customers within a single route. This strategy helps optimize delivery efficiency, reduce operational costs, and make each delivery more profitable by serving multiple customers in a given area during a single trip.
3. How can I optimize delivery times for my hyperlocal business?
To optimize delivery times in a hyperlocal business, consider using advanced route planning platforms. These platforms empower businesses to create highly efficient routes, minimizing the time it takes to deliver from the store to the customer's address. This, in turn, reduces the chances of delays and diversions, enhancing overall operational efficiency.
4. How can technology contribute to a seamless hyperlocal delivery experience?
Technology plays a pivotal role in ensuring a seamless hyperlocal delivery experience. Route planning software helps optimize delivery routes, reducing travel time and fuel consumption. Mobile apps enhance communication between customers and delivery personnel, offering real-time tracking and updates. Integrating these technologies creates a more efficient, transparent, and customer-friendly hyperlocal delivery experience.
If you enjoyed this blog, you might also be interested in: